As more and more organizations are migrating to the cloud in support of Digital Transformation. It is safe to say that it is one of the best decisions an organization has made to be successful. Along with the migration cost, security, capacity planning in the cloud, and business goals they should also approach using the best cloud migration strategy.
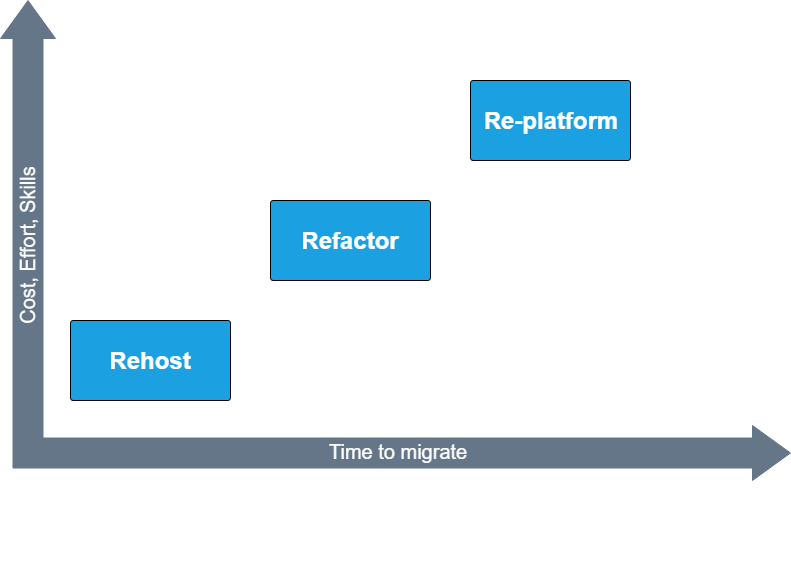
There are three different ways to approach application migrations to the cloud: Rehost (Lift and Shift), Replatform, and Refactor. Now that we know the three R’s of cloud migration strategy let’s dive deep into it.
Rehost or Lift and Shift Strategy
Moving an application or operation from one environment to another is known as Lift and Shift strategy. This involves moving workloads and tasks from on-premises to the cloud or operations can also be redeployed from one cloud to a new cloud environment.
The beginner’s tactic for quick migration to the cloud should consider Lift and Shift strategy. With lift and shift strategy, there is very little or no redesigning the application, but you may need to change the host configuration if the application is shifting to a new cloud environment. This method offers a quick and easy migration solution with minimal disruption.
Some organization use rehost strategy first to migrate to the cloud and then they will re-architect to optimize the application. Using this strategy saves both the cost and redesigning time while replicating on-premises to the cloud.
You can use AWS automation tools such as AWS VM import/export or Racemi if you decide to migrate to AWS.
When to use Rehost of Lift and Shift Strategy?
- Organizations that are spending too much money to maintain physical infrastructure and would like to reduce this cost can approach the rehost method.
- Organizations can use this approach if cost and time to migrate is their prime concern.
- Organizations having applications in their on-premises and are considering to move to the cloud without any modification or disruption, then adopting the rehost method is a wise choice.
- It is easy to optimize some applications after migrating to the cloud, such applications should be migrated using the rehost method and then optimize it.
- If the applications are very complex and impossible to recode then using rehost is the best option.
- An organization that is already in the cloud and faced with disaster, should use rehost strategy to perform recovery and run the application in a short period to time.
Re-platform Strategy
The re-platform strategy involves a little optimization before finally migrating it to the cloud. Experts suggest that a small optimization can harness significant benefits without changing the core architecture of the application.
Often times when organizations have legacy applications that can’t be simply migrated up to IaaS cloud, it is possible to run those applications on cloud servers using the emulators. An example of this is Microsoft Windows Server 2012. Microsoft Windows 2012 natively supports 32-bit applications even though the operating system is 64 bit.
While managing DB in your existing on-premises environment which takes up most of the time can benefit AWS cloud’s auto scaling feature and managed DB services. By using AWS managed DB, an organization can save a significant amount of time.
The re-platform strategy offers developers to reuse the resources they are comfortable to work with legacy programming languages, caches in the application, and frameworks.
When to use Replatform Strategy?
- Enterprises looking out to gain more benefits from the cloud than just migrating to the cloud.
- Organizations leveraging automation tasks that are being offered by cloud providers.
- Organizations that have applications which don’t require recoding or changing core architecture.
- If the on-premises scaling is getting complex and expensive, then considering re-platform is a good decision.
- An organization willing to perform slight changes and automate tasks should consider re-platform.
Refactor or Rearchitect Strategy
Refactor or Rearchitect strategy is a complex approach than the above two strategies since this involves making major changes in the application configuration and changing the code of the application. Also one has to account that the behavior of the applications remains same.
Applications that are refactored sees the benefit of reduced costs, reduced operational requirements, increased scalability and uptimes.
Depending upon the business needs, you can either choose partial or complete refactor. In the partial refactor, you can migrate quickly compared to complete refactor as it involves a small change in the application.
Wherein a complete refactor involves modifying the application completely. This can be beneficial by getting higher performance at reduced cost.
When to use Refactor or Rearchitect Strategy?
- An organization that is looking to scale their existing on-premises application.
- When there is a strong need for adding new features and increase performance of the application, one has to use refactor strategy.
- Restructuring of the code to take complete benefit of the cloud.
- If the organization is willing to move to a service-oriented architecture, then refactor is the best approach.
Analysing your complete IT environment can help you identify infrastructure and application workloads. We highly recommend performing this analysis before considering the migration strategy.
After the analysis, you can determine which strategy to consider to get the most of the cloud benefits.
About InterPole
InterPole was established in 1996 and engages in web hosting, email, and management of IT infrastructure. InterPole pioneered with Virtual Private Servers in 2004 and Cloud Hosting in 2008. Over the years, InterPole has worked with over 6200 mid-sized businesses and startups, and have assisted them in their journey towards the adoption of modern technologies through the Internet. InterPole is a Standard Consulting Partner of Amazon AWS and Microsoft Azure. With this partnership, provides Managed AWS service and maintains a team of engineers who are trained and certified for the specific cloud platforms. These benefits companies in defining their cloud strategy and making a well-planned journey, reliably and cost-effectively.

